1. Gene, DNA and Chromosomes
- Genes
- Genes are sections of DNA that code for the production of protein and are arranged along the chromosomes.
- Carry the inherited characteristics of a person.
- Genes occurs in pairs, therefore each inherited characteristics is carried by two genes.
- One gene from each pair comes from the father and the mother.
- Example of inherited characteristics carried by genes are colour of the eyes, pattern of finger prints, type of hair, blood group and etc.

- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acids)
- A double helix, made up of a series of genes to encode genetic information.
- This determine the individual characteristics of an organism.
- All the information in DNA is transmitted in the form of a genetic code.
- Should any information not be followed, the baby will be born with physical or mental defects.
- DNA molecule is very complicated and resembles a twisted ladder or staircase.

- Chromosomes
- Is a thread-like structure found in the nucleus of a cell.
- Chromosomes and the genes on them are composed of DNA.
- It exist in pair and are identical-->homologous.
- A pair of chromosomes has genes arranged in the same way. As a result the genes also exist in pairs.
- Human has two sets of chromosomes in the body(one set from the father and another set form the mother).
2. Mitosis
- Mitosis is occur in somatic cells --> all cells body except reproductive cells.
- Mitosis is the type of cell division that produces genetically identical cells.
- During mitosis, DNA replicates in the parent cell, which divides to produce two new cells, each containing an exact copy of the DNA as in the parent cell.
- This allows growth of multicellular organism from unicellular zygotes.
- Mitosis is the basis of asexual reproduction --> the production of new individuals of a species by one parent organism.
- Cells produced are diploid (2n).
- Replacement of cells and repair of tissues is possible through mitosis. For example, cell replacement is rapid in the skin & in the lining of the gut.
- Mitosis is actively carried out at the ends of plant shoots and roots.
- Mitosis is divided into four phases.
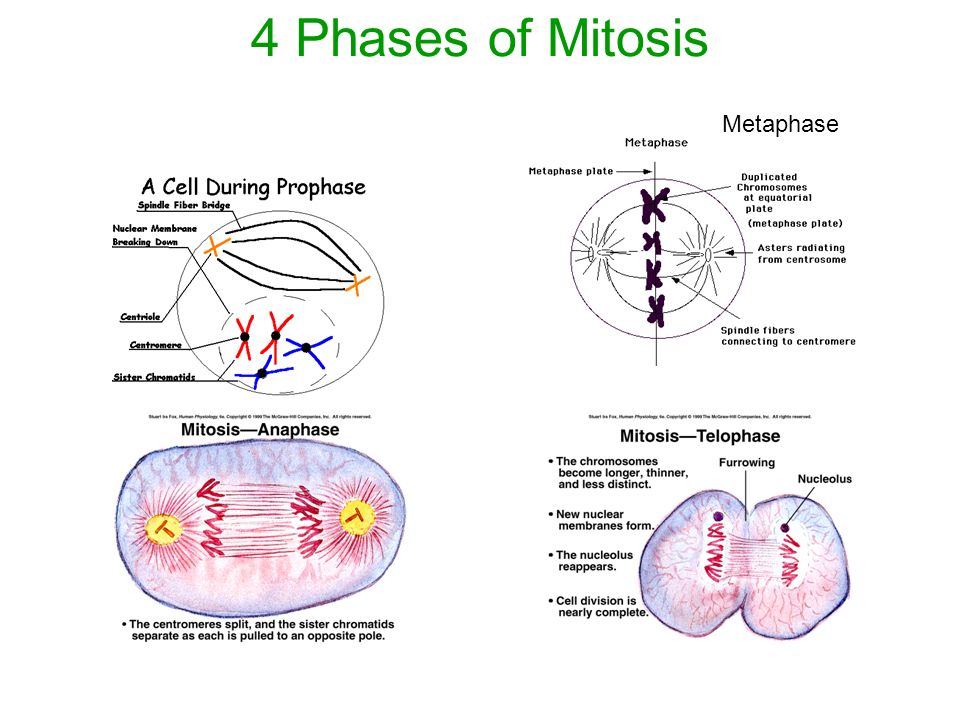
- To understand more about mitosis, please watch this video:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DwAFZb8juMQ
3. Meiosis
- Meiosis is the process by which a nucleus divides by two divisions into four nuclei, each containing half the number of chromosome of the mother cell.
- Resulting nuclei are haploid (n).
- The cells produced are genetically different to the parent cell and to each other.
- Occurs in 2 stages that is meiosis 1 and meiosis 2.
- Produces genetic variation (caused by crossing over between homologous chromosome).
- In animals, meiosis occurs in testes and ovaries, whereas in plants, it occurs in the anthers and ovaries.

- To understand more about meiosis, please watch this video:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7EvtgLLuJpo
- Go to joinmyquiz.com
- Code: 997504
DAY 3: Inheritance
1. Inheritance
- In order for you to do this activity, please read the subtopic Inheritance in your textbook.
- Watch any video in the Youtube and do research in the internet to get more information about inheritance.
- Answer the questions below in foolscap paper.
1. Diagram below shows the sex determination in human
- Name the process of J and K.
- What is the gender of zygote R?
- How many chromosomes in zygote T?
2. Diagram below shows schematic diagram for hair types.
- Complete the genotype of the children.
- Which hair is dominant?
3. Draw a schematic diagram of:
- TT x tt
- Tt x Tt
- TT x Tt


No comments:
Post a Comment